Concept of HVDC
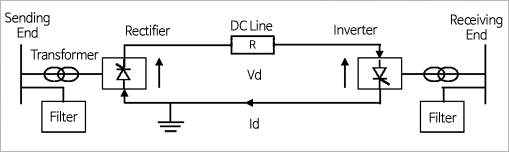
- High Voltage Direct Current Transmission
- A technology enabling direct current electric power transmission after converting from alternating current(AC) to direct current(DC), or vice versa.
Advantages of HVDC
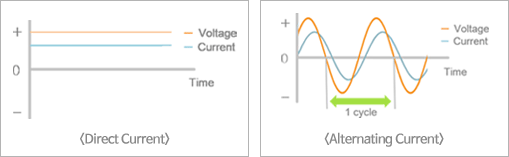
- Large-scale power transmission for a long distance
- While AC is unstable due to reactive power, HVDC is not affected by reactive power flow, without distance limits for power transmission.
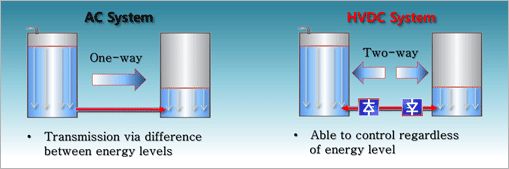
- Availability to control interchange power, Improvement of system stability
- HVDC can be applied to any rated voltage and frequency, facilitating to realize specific function to improve reliability of the network Moreover, interconnection of systems can be stably operated through HVDC since a failure in one system does not affect the other.
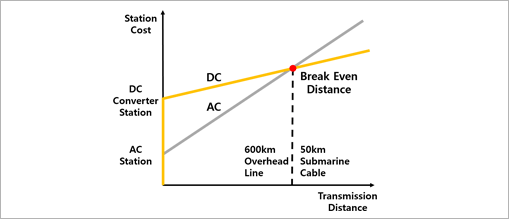
- Efficiency
- While it costs more to start up, HVDC is more cost-efficient than AC transmission, reducing size of steel towers and number of conductors, and not requiring a reactive power compensator. HVDC transmission is more economical than AC when built over the break-even distance(Approx. 600km for overhead line, 50km for submarine line).
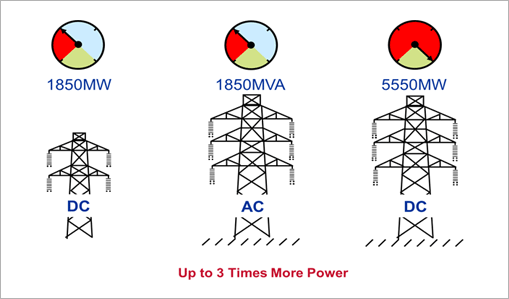
- Decrease of footprint
- HVDC transmission system has a simpler insulation design, so the steel tower can transport 3 times more power than that of AC steel tower of the same size. This decreases the number and size of transmission facility to resolve our social issues regarding electrical construction.
Future Power Grid
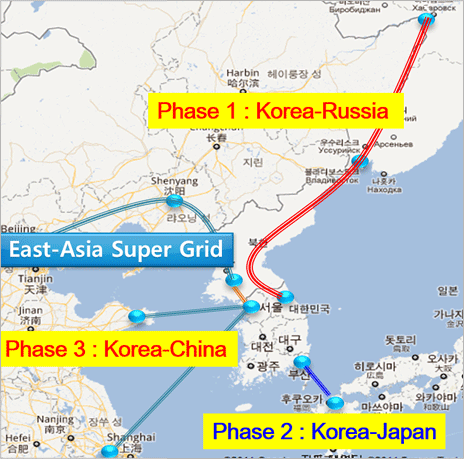
- Interconnection of power system over countries
(East-Asia Super Grid)
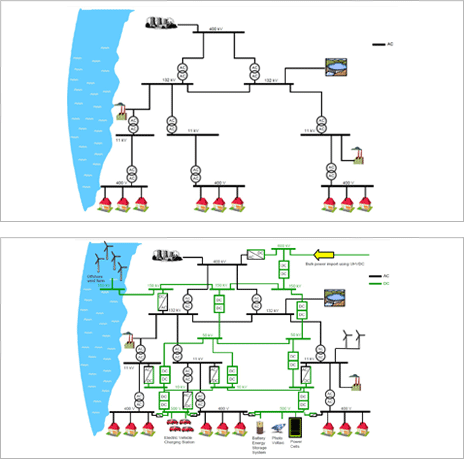
- Single AC Network + HVDC System = Hybrid Power Grid

